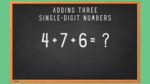Mathematics – United States – Common Core State Standards
1.OA – Operations & Algebraic Thinking
Mathematics
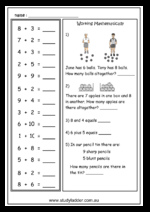
1.OA.1 – Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. (See Glossary, Table 1. http://www.corestandards.org/the-standards/mathematics/glossary/glossary/ )
-
9 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding 2 (number line). Adding within 5 - activity 1. Adding on to ten. Adding by counting (problem solving).
-
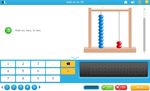
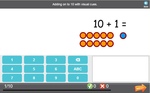
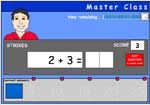
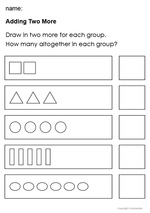
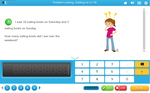
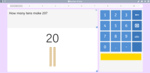
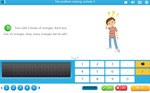
Adding two more on a number line
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Adding 2 (number line)
- Challenge
-
-
-
- ONE MINUTE CHALLENGE - Add 2
- Challenge
-
-
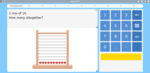
Adding within six using visual cues
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding within 5 - activity 1
- Practice
-
-
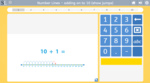
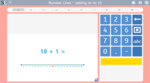
Adding-on to 10
- Activities: 7 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Adding on to ten
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 by counting
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 by counting
- Practice
-
-
-
- Number Lines - adding on to 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding on to 10 using a number line
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 with visual cues.
- Practice
-
-
-
- Add on to 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Add on to 10
- Printable
-
-
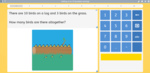
Single-digit addition problem solving using visual cues
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding by counting (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding by counting (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
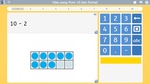
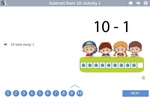
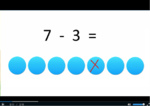
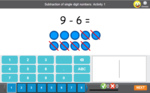
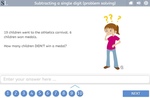
Subtracting from 10
- Activities: 7 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtraction from 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract - numbers under 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtract - numbers under 10
- Practice
-
-
Adding single-digit numbers - number skills
- Activities: 7 course, 17 extra
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-
- Add numbers less than 5
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add doubles - single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Timed Challenge: Add numbers less than 5
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Add Single Digits Duck Game
- Practice
-
-
-
- Drill - Add numbers up to 10.
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Doubles to 20
- Printable
-
-
-

- Drill - Doubles to 20 (Auto-Generated)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition to 20 - with visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Add numbers less than 5
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Add single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

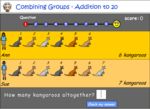
- Combining to 20
- Practice
-
-
Make 10.
- Activities: 6 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 (20 questions)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 - Using a number line
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Make 10 - Visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Combination to 10
- Practice
-
-
Subtraction using visual cues. - How Many Left?
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
Extra activities
-
-

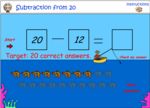
- Subtract from 20
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtraction using a number line
- Practice
-
-
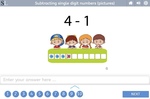
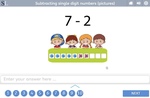
Subtracting single-digit numbers
- Activities: 4 course, 12 extra
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtraction problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Subtraction under 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtract single digits
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Subtract from 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract numbers less than 20
- Assessment
-
-
-
9 learning outcomes – click to view
1.OA.2 – Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding three numbers (small numbers). Adding three single digit numbers. Adding three numbers (small numbers).
-
Adding three small numbers
- Activities: 2 course, 10 extra
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Add three numbers - each under 6
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Printable
-
-
-

- Add three numbers - each under 6
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Add three single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
Adding three numbers
- Activities: 7 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Adding three single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Add three sets of numbers
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding three numbers (small numbers)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding three numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add three single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
1.OA.3 – Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract. (Students need not use formal terms for these properties.) Examples: If 8 + 3 = 11 is known, then 3 + 8 = 11 is also known. (Commutative property of addition.) To add 2 + 6 + 4, the second two numbers can be added to make a ten, so 2 + 6 + 4 = 2 + 10 = 12. (Associative property of addition.)
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding by counting (printable). Adding on to ten. Adding single digit numbers.
-
Adding to ten using visual cues
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding by counting (printable)
- Printable
-
-
-

- Add on to 5
- Practice
-
-
-

- Addition of numbers less than 5
- Practice
-
-
Adding-on to 10
- Activities: 7 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Adding on to ten
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 by counting
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 by counting
- Practice
-
-
-
- Number Lines - adding on to 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding on to 10 using a number line
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 with visual cues.
- Practice
-
-
-
- Add on to 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Add on to 10
- Printable
-
-
Adding single-digit numbers - number skills
- Activities: 7 course, 17 extra
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-
- Add numbers less than 5
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add doubles - single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Timed Challenge: Add numbers less than 5
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Add Single Digits Duck Game
- Practice
-
-
-
- Drill - Add numbers up to 10.
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Doubles to 20
- Printable
-
-
-

- Drill - Doubles to 20 (Auto-Generated)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition to 20 - with visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Add numbers less than 5
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Add single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Combining to 20
- Practice
-
-
Single-digit addition (missing number)
- Activities: 5 course, 10 extra
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition with a missing number
- Assessment
-
-
Subtracting from 10
- Activities: 7 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtraction from 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract - numbers under 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtract - numbers under 10
- Practice
-
-
Subtracting single digit numbers - visual
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Subtracting single-digit numbers
- Activities: 4 course, 12 extra
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtraction problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Subtraction under 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtract single digits
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Subtract from 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract numbers less than 20
- Assessment
-
-
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
1.OA.4 – Understand subtraction as an unknown-addend problem. For example, subtract 10 – 8 by finding the number that makes 10 when added to 8. Add and subtract within 20.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Make 10. Make 10 (problem solving). Single digit addition (missing number). Addition - missing numbers. Make 10.
-
Make 10.
- Activities: 6 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 (20 questions)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 - Using a number line
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Make 10 - Visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Combination to 10
- Practice
-
-
Make 10 (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving) Answer sheet
- Printable
-
-
Single-digit addition (missing number)
- Activities: 5 course, 10 extra
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition with a missing number
- Assessment
-
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
1.OA.5 – Relate counting to addition and subtraction (e.g., by counting on 2 to add 2).
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: One and two more than. One and two less than. Two more than. Count on and back by 2. Subtract 1 from numbers under 10.
-
One more than
- Activities: 6 course, 3 extra
-
-
- One and two more than
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- One more than
- Practice
-
-
-
- One more than - number line
- Practice
-
-
-
- One more than - problem solving
- Practice
-
-
-
- One More Than
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Kevin Captivate Test
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- TEST
- Practice
-
-
-
- ONE MINUTE CHALLENGE - Adding 1
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Next number - numbers up to 20
- Assessment
-
-
One less than
- Activities: 3 course, 2 extra
-
-
- One and two less than
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- One less
- Practice
-
-
-
- One Less Than
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- One less than
- Printable
-
-
Two more than
- Activities: 4 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Two more than
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Two more than
- Practice
-
-
-
- Two more than - number line
- Practice
-
-
-
- Two more than - problem solving
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Two more than
- Printable
-
-
-
- Count on 2 - numbers up to 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Count on 2 - numbers up to 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Count on 2 - numbers up to 20
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Count on 2 - numbers up to 10
- Tutorial
-
-
Two less than
- Activities: 2 course, 3 extra
-
-
- Count on and back by 2
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Two less than
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract 2 from numbers under 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Numbers
- Assessment
-
-
Take one away
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Subtract 1 from numbers under 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtract 1 from numbers under 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtract 1 from numbers under 10
- Practice
-
-
Subtracting 2
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Subtracting 2
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting 2
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting 2 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
-
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
1.OA.6 – Add and subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency for addition and subtraction within 10. Use strategies such as counting on; making ten (e.g., 8 + 6 = 8 + 2 + 4 = 10 + 4 = 14); decomposing a number leading to a ten (e.g., 13 – 4 = 13 – 3 – 1 = 10 – 1 = 9); using the relationship between addition and subtraction (e.g., knowing that 8 + 4 = 12, one knows 12 – 8 = 4); and creating equivalent but easier or known sums (e.g., adding 6 + 7 by creating the known equivalent 6 + 6 + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13).
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding single digit numbers. Subtracting single digit numbers. Adding single digit numbers (problem solving).
-
Adding single-digit numbers - number skills
- Activities: 7 course, 17 extra
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-
- Add numbers less than 5
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add doubles - single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Timed Challenge: Add numbers less than 5
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Add Single Digits Duck Game
- Practice
-
-
-
- Drill - Add numbers up to 10.
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Doubles to 20
- Printable
-
-
-

- Drill - Doubles to 20 (Auto-Generated)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition to 20 - with visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Add numbers less than 5
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Add single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Combining to 20
- Practice
-
-
Subtracting single-digit numbers
- Activities: 4 course, 12 extra
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtraction problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Subtraction under 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtract single digits
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Subtract from 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract numbers less than 20
- Assessment
-
-
Adding single-digit numbers- problem solving
- Activities: 4 course, 9 extra
-
Make 10 (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Make 10 (problem solving) Answer sheet
- Printable
-
-
Subtracting single digits from up to 20 (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 7 extra
-
-
- Single digit subtraction
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Single digit subtraction
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit subtraction Answer sheet
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition and subtraction problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Subtraction problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
1.OA.7 – Understand the meaning of the equal sign, and determine if equations involving addition and subtraction are true or false. For example, which of the following equations are true and which are false? 6 = 6, 7 = 8 – 1, 5 + 2 = 2 + 5, 4 + 1 = 5 + 2.
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding single digit numbers. Adding single digits (matching answers). Adding single digits (matching answers).
-
Adding single digit numbers - matching answers
- Activities: 4 course, 1 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
1.OA.8 – Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 + ? = 11, 5 = _ – 3, 6 + 6 = _.
-
12 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Make 10. Single digit addition (missing number). Single digit subtraction (missing number). Adding 2 (number line).
-
Make 10.
- Activities: 6 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 (20 questions)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Make 10 - Using a number line
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Make 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Make 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Make 10 - Visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Combination to 10
- Practice
-
-
Single-digit addition (missing number)
- Activities: 5 course, 10 extra
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Single digit addition (missing number)
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition with a missing number
- Assessment
-
-
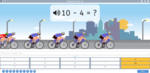
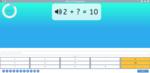
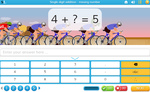
Adding two more on a number line
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Adding 2 (number line)
- Challenge
-
-
-
- ONE MINUTE CHALLENGE - Add 2
- Challenge
-
-
Adding within six using visual cues
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding within 5 - activity 1
- Practice
-
-
Adding-on to 10
- Activities: 7 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Adding on to ten
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 by counting
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 by counting
- Practice
-
-
-
- Number Lines - adding on to 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding on to 10 using a number line
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding on to 10 with visual cues.
- Practice
-
-
-
- Add on to 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Add on to 10
- Printable
-
-
Adding single-digit numbers - number skills
- Activities: 7 course, 17 extra
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-
- Add numbers less than 5
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add doubles - single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Timed Challenge: Add numbers less than 5
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Add Single Digits Duck Game
- Practice
-
-
-
- Drill - Add numbers up to 10.
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Doubles to 20
- Printable
-
-
-

- Drill - Doubles to 20 (Auto-Generated)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Addition to 20 - with visual cues
- Practice
-
-
-

- Add numbers less than 5
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Add single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Combining to 20
- Practice
-
-
Subtracting from 10
- Activities: 7 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtraction from 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting from 10
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract - numbers under 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtract - numbers under 10
- Practice
-
-
Subtracting single digit numbers - visual
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Subtracting single-digit numbers
- Activities: 4 course, 12 extra
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtraction problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - Subtraction under 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract single digit numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtract single digits
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Subtract from 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Subtract single digit numbers
- Practice
-
-
-

- Subtract numbers less than 20
- Assessment
-
-
Balancing equations - Equivalent number sentences
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Balancing equations - addition
- Practice
-
-
-
- Balancing equations - subtraction
- Practice
-
-
-
- Balancing equations - addition
- Practice
-
-
-
12 learning outcomes – click to view
1.NBT – Number & Operations in Base Ten
Mathematics
1.NBT.1 – Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120. In this range, read and write numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral.
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Counting to 100. Counting to 100 (number line 30-50). Missing numbers. Counting to 100 (number line 50-70).
-
Counting to 100 using a hundreds chart
- Activities: 6 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Counting to 100
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Missing numbers
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Hundreds chart 1-30
- Practice
-
-
-
- Hundreds chart 31-60
- Practice
-
-
-
- Hundreds chart 61-100
- Practice
-
-
-
- Hundred's Chart Count
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Hundred's Chart
- Printable
-
-
-

- Number Chart 1 - 100
- Whiteboard
-
-
Counting to one hundred on a number line
- Activities: 3 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Counting to 100 (number line 30-50)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting to 100 (number line 50-70)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting to 100 (number line 70-100)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Numbers Problem Solving
- Printable
-
-
-

- Count to 100
- Practice
-
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
1.NBT.2 – Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases:
1.NBT.2.a – 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones — called a “ten.”
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Place Value Teens Mab using blocks to count. Counting to 20 using cubes. Counting to 30 using cubes.
-
Place value (11-20)
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Place value - tens and ones (to 100)
- Activities: 8 course, 3 extra
-
-
- Representing place value - to 100
- Printable
-
-
-
- Place Values
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Place Values
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Tens and ones - numbers up to 100
- Printable
-
-
-

- Identifying Place Value
- Practice
-
-
-

- Guessing game - Numbers to 100
- Practice
-
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
1.NBT.2.b – The numbers from 11 to 19 are composed of a ten and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones.
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Place Value Teens Mab using blocks to count. Counting to 20 using cubes.
-
Place value (11-20)
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
1.NBT.2.c – The numbers 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine tens (and 0 ones).
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Counting on number line (by 10's). Counting by 10. Counting by 10. Counting by 10. Counting by 10. Counting by 10.
-
Counting on by ten on a number line
- Activities: 6 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Counting on number line (by 10's)
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Numbers Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Count by lots of 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Counting by 10
- Assessment
-
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
1.NBT.3 – Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <.
Mathematics
1.NBT.4 – Add within 100, including adding a two-digit number and a one-digit number, and adding a two-digit number and a multiple of 10, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. Understand that in adding two-digit numbers, one adds tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose a ten.
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Place value - adding on ones. Adding on 10 using blocks. Adding multiples of 10 using blocks.
-
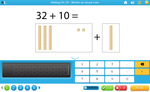
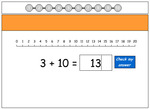
Place value - adding 10
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
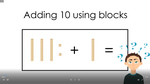
- Adding on 10 using blocks
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on 10 using blocks
- Practice
-
-
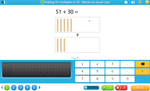
Place value - adding multiples of 10
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10 using blocks
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10 using blocks
- Practice
-
-
Place value - adding two-digit numbers
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
Show addition and subtraction visually
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
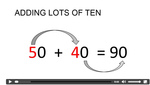
Adding multiples of 10
- Activities: 3 course, 4 extra
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10.
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding multiples of 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Addition problem solving
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Adding lots of 10
- Practice
-
-
Adding single-digit numbers to two-digit numbers
- Activities: 3 course, 14 extra
-
-
- Adding on (numbers under 10)
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on (numbers under 10)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding on (numbers under 10)
- Challenge
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding on (numbers under 10)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding on (numbers under 10)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Add on numbers under 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Add on numbers less than 10
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Add lots of 10 - Jump Strategy
- Practice
-
-
-

- Adding lots of 10 to numbers less than 200
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Adding lots of 10 to numbers less than 1,000
- Assessment
-
-
Adding multiples of 10
- Activities: 1 course, 3 extra
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
1.NBT.5 – Given a two-digit number, mentally find 10 more or 10 less than the number, without having to count; explain the reasoning used.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding 10. Subtracting 10 using blocks. Subtracting 10. Counting on number line (by 10's). Groups of 10. Adding 10.
-
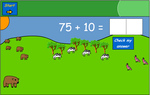
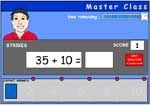
Adding 10 to two-digit numbers
- Activities: 6 course, 14 extra
-
-
- Adding 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Adding on 10 using blocks
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding 10 to numbers up to 100
- Practice
-
-
-
- Adding 10 (to two digits)
- Challenge
-
-
-
- Counting Forwards By 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Adding 10 (numbers up to 20)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Adding 10 (numbers up to 100)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill - add on 10 to numbers up to 20
- Printable
-
-
-
- Drill Add On 10 to numbers Less 100
- Printable
-
-
-

- Add on 10 - Jump Strategy
- Practice
-
-
Subtracting 10
- Activities: 7 course, 12 extra
-
-
- Subtracting 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtract 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10 (problem solving)
- Practice
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10
- Challenge
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Subtracting 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10 (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtracting 10 (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract 10 from numbers under 100
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract 10 from larger numbers
- Printable
-
-
-
- Subtract 10 from numbers
- Printable
-
-
-

- Subtract 10 from larger numbers
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Subtract 10 from larger numbers
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Subtract 10 from numbers
- Assessment
-
-
Counting on by ten on a number line
- Activities: 6 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Counting on number line (by 10's)
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Numbers Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Count by lots of 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Counting by 10
- Assessment
-
-
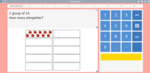
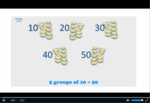
Groups of ten
- Activities: 6 course, 5 extra
-
-
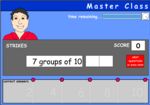
- Groups of 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Number of tens
- Practice
-
-
-
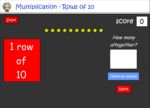
- Rows of 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Rows Of 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Groups of 10
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Rows of ten
- Practice
-
-
-

- Groups of 10
- Assessment
-
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
1.NBT.6 – Subtract multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 from multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 (positive or zero differences), using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Subtracting multiples of 10 using blocks. Counting on number line (by 10's). Groups of 10.
-
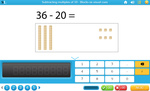
Place value - subtracting multiples of 10
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Counting on by ten on a number line
- Activities: 6 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Counting on number line (by 10's)
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Counting by 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Numbers Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Count by lots of 10
- Practice
-
-
-

- Counting by 10
- Assessment
-
-
Groups of ten
- Activities: 6 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Number of tens
- Practice
-
-
-
- Rows of 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Practice
-
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Rows Of 10
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Printable
-
-
-
- Groups of 10
- Printable
-
-
-

- Groups of 10
- Challenge
-
-
-

- Rows of ten
- Practice
-
-
-

- Groups of 10
- Assessment
-
-
10x tables (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 6 extra
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Practice
-
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
- 10x tables (problem solving)
- Printable
-
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
1.MD – Measurement & Data
Mathematics
1.MD.1 – Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Measuring Length (using informal units). Order or compare objects or shapes based on informal measurements.
-
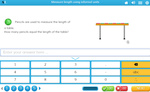
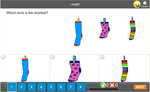
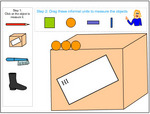
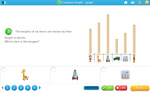
Measure length using informal units.
- Activities: 2 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Measure length using informal units
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Length
- Practice
-
-
-

- Length
- Assessment
-
-
-

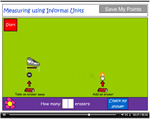
- Measuring using informal units
- Practice
-
-
-

- Using informal units to measure length.
- Whiteboard
-
-
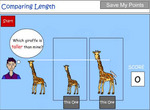
Order objects based on length.
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
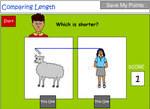
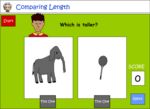
Directly compare length
- Activities: 1 course, 5 extra
-
-
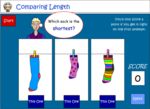
- Compare length (taller-shorter)
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
Compare the length of three objects
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
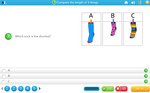
- Compare the length of 3 things
- Practice
-
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
1.MD.2 – Express the length of an object as a whole number of length units, by laying multiple copies of a shorter object (the length unit) end to end; understand that the length measurement of an object is the number of same-size length units that span it with no gaps or overlaps. Limit to contexts where the object being measured is spanned by a whole number of length units with no gaps or overlaps.
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Measuring Length (using informal units). Order or compare objects or shapes based on informal measurements.
-
Measure length using informal units.
- Activities: 2 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Measure length using informal units
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Length
- Practice
-
-
-

- Length
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Measuring using informal units
- Practice
-
-
-

- Using informal units to measure length.
- Whiteboard
-
-
Order objects based on length.
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Compare the length of three objects
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Compare the length of 3 things
- Practice
-
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
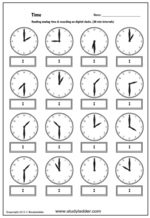
1.MD.3 – Tell and write time in hours and half-hours using analog and digital clocks.
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Reading the time on a clock. Telling the time - half past. Telling the time on an analog clock - o'clock.
-
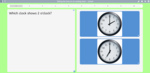
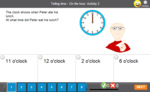
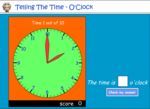
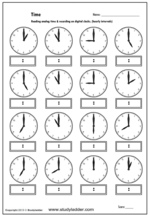
Telling the time on an analog clock - o'clock
- Activities: 4 course, 8 extra
-
-
- Reading the time on a clock
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Matching activity - o'clock times
- Printable
-
-
-
- Reading An Analog Clock
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Reading an analog clock - o'clock
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Reading an analog clock - o'clock
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Reading an analog clock - o'clock Part 1
- Printable
-
-
-
- Reading an analog clock - o'clock Part 2
- Printable
-
-
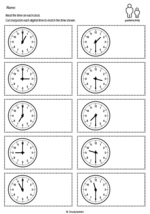
Telling the time on an analog clock - half past
- Activities: 5 course, 8 extra
-
-
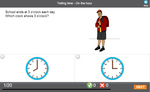
- Telling the time - half past
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Timeline - O'clock and half past
- Printable
-
-
-
- O'clock and half past
- Printable
-
-
-
- Reading A Clock Half Past
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Reading a clock - half past the hour
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Reading a clock - half past the hour
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Reading a clock - half past the hour
- Practice
-
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
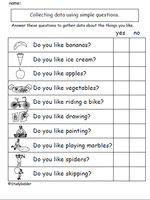
1.MD.4 – Organize, represent, and interpret data with up to three categories; ask and answer questions about the total number of data points, how many in each category, and how many more or less are in one category than in another.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Answer simple questions to collect data. Using simple questions to gather data. version in next outcome.
-
Answer yes/no questions to collect data
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
Extra activities
-
-
- Answer yes/no questions to collect data
- Printable
-
-
Display data with objects and drawings
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
Extra activities
-
-
- version in next outcome
- Printable
-
-
-
- version in next outcome
- Printable
-
-
Interpret data presented using drawings and symbols
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Interpret data as drawings
- Practice
-
-
-
- Interpret data as drawings
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Display data using objects and drawings
- Printable
-
-
-
- Display data using objects and drawings
- Printable
-
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
1.G – Geometry
Mathematics
1.G.1 – Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles are closed and three-sided) versus non-defining attributes (e.g., color, orientation, overall size) ; build and draw shapes to possess defining attributes.
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Naming shapes - objects. Sorting two-dimensional shapes. Quadrilaterals. Drawing shapes.
-
Naming shapes in objects
- Activities: 1 course, 6 extra
-
-
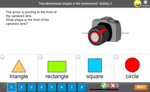
- Naming shapes - objects
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
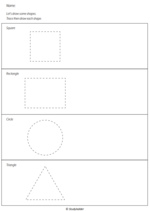
- Drawing shapes
- Printable
-
-
-
- Identifying shapes
- Printable
-
-
-

- Using shapes to construct a picture
- Practice
-
-
-

- Manipulating Shapes 2
- Practice
-
-
-

- Design using 2D shapes
- Practice
-
-
Sorting two-dimensional shapes
- Activities: 3 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Sorting two-dimensional shapes
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Classify two-dimensional shapes
- Practice
-
-
-
- Classify two-dimensional shapes
- Practice
-
-
-

- Sort 2D shapes - number of corners
- Practice
-
-
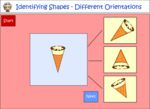
Identifying two-dimensional shapes
- Activities: 5 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Quadrilaterals
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Naming two-dimensional shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Regular and irregular shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Identifying two-dimensional shapes
- Practice
-
-
-
- Naming two-dimensional shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
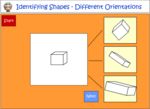
1.G.2 – Compose two-dimensional shapes (rectangles, squares, trapezoids, triangles, half-circles, and quarter-circles) or three-dimensional shapes (cubes, right rectangular prisms, right circular cones, and right circular cylinders) to create a composite shape, and compose new shapes from the composite shape.(Students do not need to learn formal names such as “right rectangular prism.”)
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Environmental objects. Dividing shapes. Joining 3D objects to make composite objects. Quadrilaterals.
-
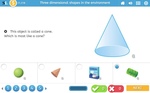
Three-dimensional objects in the environment
- Activities: 4 course, 2 extra
-
-
- Environmental objects
- Practice
-
-
-
- Environmental objects
- Practice
-
-
-
- 3D objects Hunt
- Printable
-
Extra activities
-
Identifying two-dimensional shapes
- Activities: 5 course, 0 extra
-
-
- Quadrilaterals
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Naming two-dimensional shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Regular and irregular shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Identifying two-dimensional shapes
- Practice
-
-
-
- Naming two-dimensional shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
Construct and draw two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
-
- Constructing 2D shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Constructing 2D shapes
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Drawing shapes
- Printable
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Drawing 2D shapes
- Printable
-
-
-

- Constructing 2D shapes
- Practice
-
-
-

- Draw Shapes
- Printable
-
-
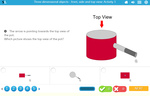
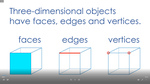
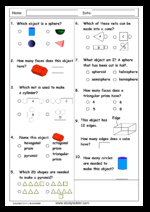
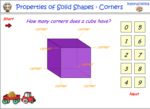
Describe the features of three-dimensional objects
- Activities: 4 course, 8 extra
-
-
- Identifying corners on 3D objects
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-

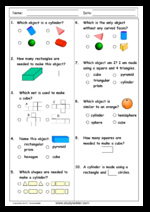
- Space 3D Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
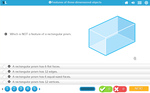
-
- Space 3D Problem Solving
- Printable
-
-
-

- Space 3D Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Space 3D Problem Solving
- Printable
-
-
-
- Properties of 3D objects
- Printable
-
-
-

- Identifying faces on 3D objects
- Practice
-
-
-

- Identifying corners on 3D Objects
- Practice
-
-
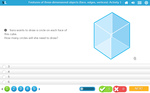
Nets of three dimensional objects
- Activities: 4 course, 4 extra
Extra activities
-
-

- Space 3D Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
- Space 3D Problem Solving
- Printable
-
-
-

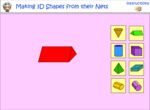
- Recognizing the nets of 3D objects
- Practice
-
-
-

- Creating 3D Objects from their nets
- Practice
-
-
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
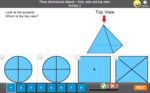
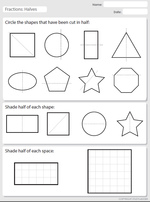
1.G.3 – Partition circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, fourths, and quarters, and use the phrases half of, fourth of, and quarter of. Describe the whole as two of, or four of the shares. Understand for these examples that decomposing into more equal shares creates smaller shares.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: A half. Quarters. Introduction to Fractions. Fractions of groups. A half. Eighths. Halves, thirds and quarters.
-
Halving objects
- Activities: 4 course, 3 extra
-
-
- A half
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- A half
- Practice
-
-
-
- Recognizing halves
- Printable
-
-
-
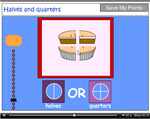
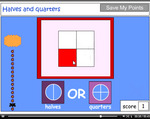
- Halves and quarters
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Matching halves
- Printable
-
-
-

- Halves - identifying an equal share
- Practice
-
-
-
- fractions test
- Practice
-
-
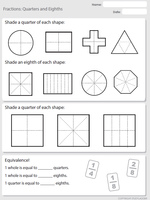
Halves, quarters and eighths
- Activities: 7 course, 10 extra
-
-
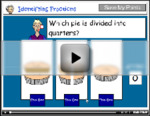
- Quarters
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Eighths
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Halves and Quarters
- Practice
-
-
-
- Halves and quarters
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Identifying Fractions
- Tutorial
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Quarters and eighths
- Printable
-
-
-
- Identifying fractions tutorial
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Halves and quarters tutorial
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Fraction of objects and shapes
- Practice
-
-
-

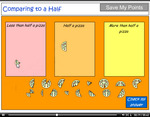
- Compare to a half tutorial
- Tutorial
-
-
-

- Compare to a half
- Practice
-
-
-

- Comparing fractions tutorial
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Identifying halves and quarters
- Practice
-
-
-

- Comparing fractions
- Practice
-
-
Halves, thirds and quarters
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
-
- Introduction to Fractions
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Halves, thirds and quarters
- Practice
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Thirds
- Printable
-
-
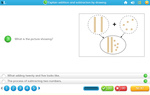
Dividing groups into halves and quarters
- Activities: 5 course, 5 extra
-
-
- Fractions of groups
- Tutorial
-
-
-
- Dividing groups into fractions
- Practice
-
-
-
- Fraction- Groups
- Printable
-
Extra activities
-
-
- Fractions
- Printable
-
-
-
- Fractions Problem Solving
- Printable
-
-
-

- Fractions
- Assessment
-
-
-

- Fractions Problem Solving
- Assessment
-
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view